## GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation
[](https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.16506)
Naive Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) methods are not aware of the topological information of the retrieved documents / knowledge graphs, and using only text information cannot solve graph question answering scenarios:
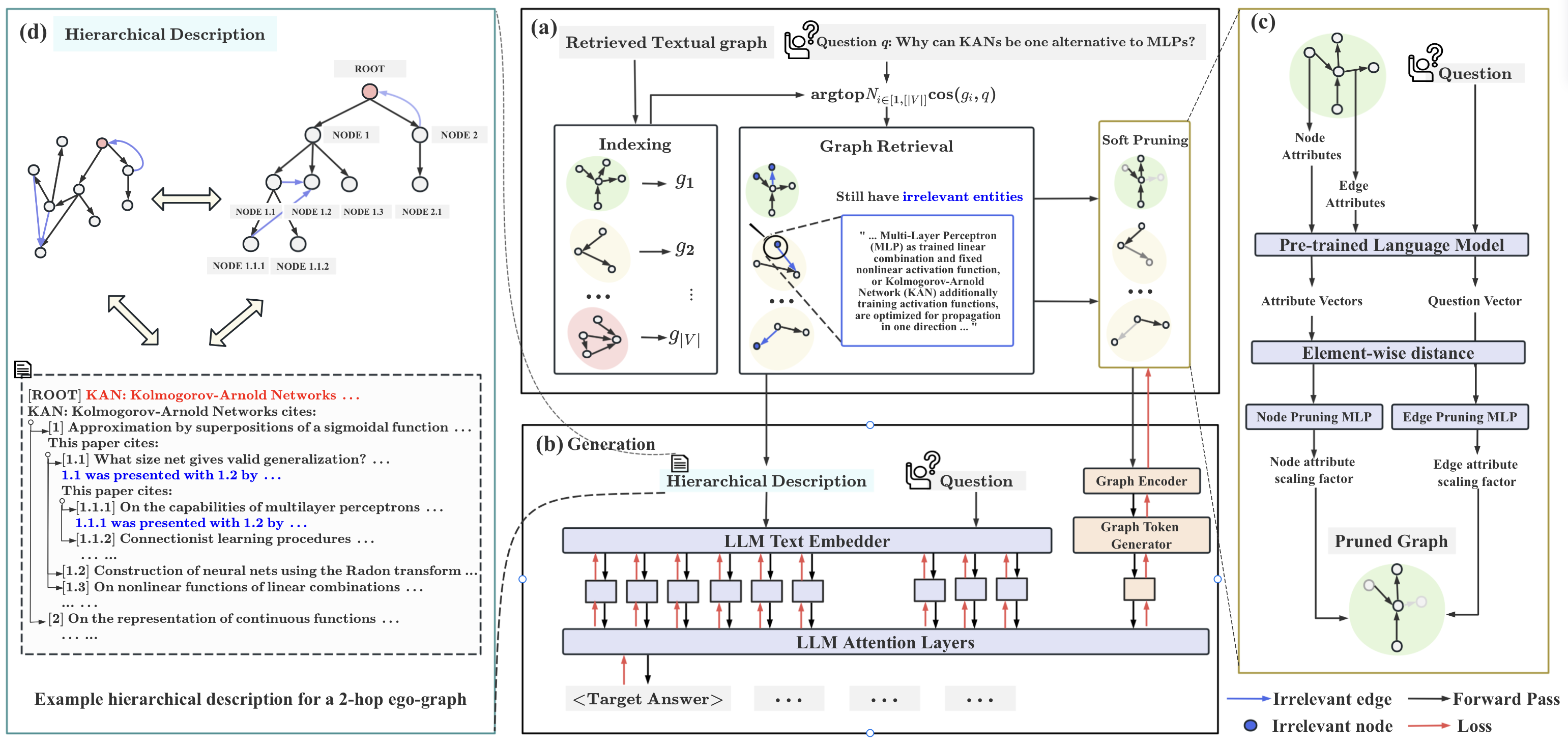
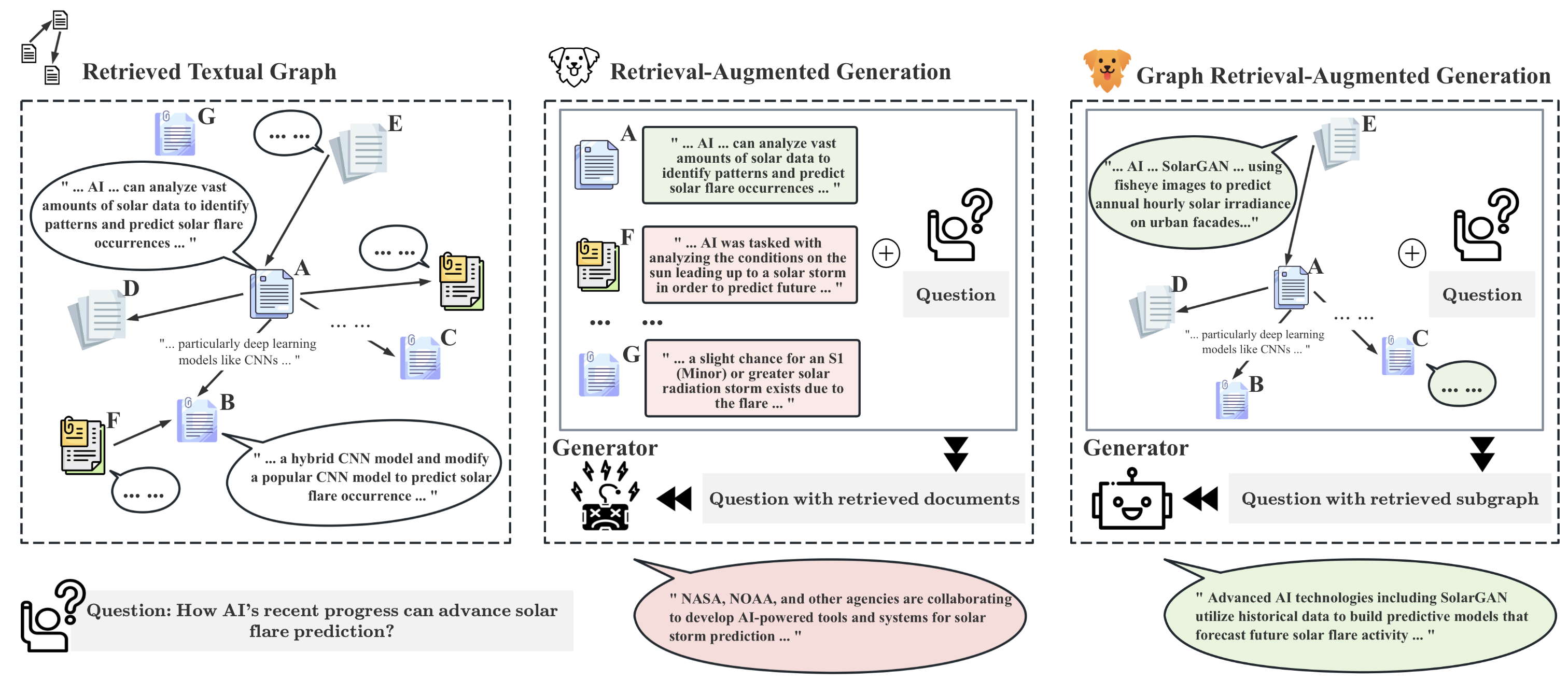 We introduce **GRAG**, retrieving relevant subgraphs instead of just discrete entities. The generation of LLM is controlled by the query and the relevant text subgraph:
We introduce **GRAG**, retrieving relevant subgraphs instead of just discrete entities. The generation of LLM is controlled by the query and the relevant text subgraph:
 ## Try GRAG
### 1) Data Preprocessing
```
python -m src.dataset.preprocess.expla_graphs
python -m src.dataset.expla_graphs
```
### Training
```
# GRAG with the frozen LLM
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm
# GRAG with fine-tuned LLM by LoRA
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm --llm_frozen False
```
## Citation
```
@article{hu2024grag,
title={GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Hu, Yuntong and Lei, Zhihan and Zhang, Zheng and Pan, Bo and Ling, Chen and Zhao, Liang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.16506},
year={2024}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
- Thanks to the [gpt-fast](https://github.com/pytorch-labs/gpt-fast) project for its code.
- Thanks to the [G-Retriever](https://github.com/XiaoxinHe/G-Retriever) contributors for their valuable work and open source contributions.
## Try GRAG
### 1) Data Preprocessing
```
python -m src.dataset.preprocess.expla_graphs
python -m src.dataset.expla_graphs
```
### Training
```
# GRAG with the frozen LLM
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm
# GRAG with fine-tuned LLM by LoRA
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm --llm_frozen False
```
## Citation
```
@article{hu2024grag,
title={GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Hu, Yuntong and Lei, Zhihan and Zhang, Zheng and Pan, Bo and Ling, Chen and Zhao, Liang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.16506},
year={2024}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
- Thanks to the [gpt-fast](https://github.com/pytorch-labs/gpt-fast) project for its code.
- Thanks to the [G-Retriever](https://github.com/XiaoxinHe/G-Retriever) contributors for their valuable work and open source contributions.
 We introduce **GRAG**, retrieving relevant subgraphs instead of just discrete entities. The generation of LLM is controlled by the query and the relevant text subgraph:
We introduce **GRAG**, retrieving relevant subgraphs instead of just discrete entities. The generation of LLM is controlled by the query and the relevant text subgraph:
 ## Try GRAG
### 1) Data Preprocessing
```
python -m src.dataset.preprocess.expla_graphs
python -m src.dataset.expla_graphs
```
### Training
```
# GRAG with the frozen LLM
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm
# GRAG with fine-tuned LLM by LoRA
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm --llm_frozen False
```
## Citation
```
@article{hu2024grag,
title={GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Hu, Yuntong and Lei, Zhihan and Zhang, Zheng and Pan, Bo and Ling, Chen and Zhao, Liang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.16506},
year={2024}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
- Thanks to the [gpt-fast](https://github.com/pytorch-labs/gpt-fast) project for its code.
- Thanks to the [G-Retriever](https://github.com/XiaoxinHe/G-Retriever) contributors for their valuable work and open source contributions.
## Try GRAG
### 1) Data Preprocessing
```
python -m src.dataset.preprocess.expla_graphs
python -m src.dataset.expla_graphs
```
### Training
```
# GRAG with the frozen LLM
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm
# GRAG with fine-tuned LLM by LoRA
python train.py --dataset expla_graphs --model_name graph_llm --llm_frozen False
```
## Citation
```
@article{hu2024grag,
title={GRAG: Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation},
author={Hu, Yuntong and Lei, Zhihan and Zhang, Zheng and Pan, Bo and Ling, Chen and Zhao, Liang},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.16506},
year={2024}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
- Thanks to the [gpt-fast](https://github.com/pytorch-labs/gpt-fast) project for its code.
- Thanks to the [G-Retriever](https://github.com/XiaoxinHe/G-Retriever) contributors for their valuable work and open source contributions.